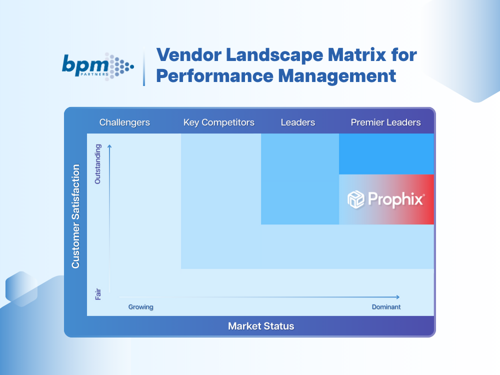
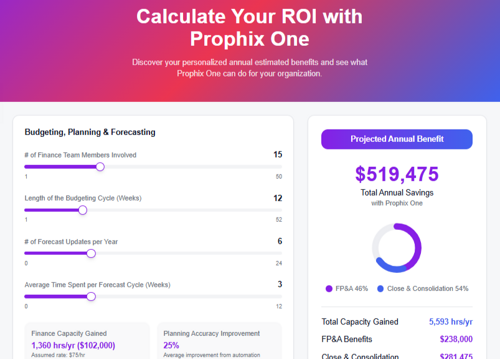
Download the BPM Partners Whitepaper
What does the federal energy regulation commission (FERC) do?
FERC regulations govern the energy industry in the United States.
June 4, 2024Imagine the vast network of the United States' energy sector as a complex electrical grid. At its heart, ensuring this network operates smoothly, fairly, and sustainably is the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC). But what exactly does this entity do?
This blog dives into FERC's role, outlines its regulations, differentiates it from NERC, explore its impact on corporate finance, and unravels its relationship with ESG, guiding you through the regulatory labyrinth.
What is the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC)?
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission, or FERC, is a 5-person regulatory agency appointed by the President of the United States with the consent of the Senate. The FERC has oversight on the Federal Power Act, the Natural Gas Act, and the Interstate Commerce Act, giving them the ability to regulate the interstate transmission of electricity, natural gas, and oil. FERC also regulates the wholesale sale of electricity but does not regulate retail electricity or natural gas sales to consumers.
What is FERC's mandate?
FERC’s mandate is to oversee proposals for the construction and operation of interstate natural gas pipelines, storage facilities, LNG (Liquified Natural Gas) terminals, and non-federal hydropower dams. This includes considering the environmental, cultural, geological, land use, and socioeconomic implications of each project.
What are FERC's responsibilities?
FERC oversees the interstate transmission of electricity, natural gas, and oil. However, the direct sale of these resources is not FERC’s responsibility and is overseen by state regulatory commissions.
What is Title 18 Chapter I?
Title 18 Chapter I refers to the first chapter within Title 18 of the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR). This chapter encompasses regulations set forth by FERC, which oversees the interstate aspects of the electricity, natural gas, and oil industries, including the conservation of power and water resources. These regulations are designed to ensure reliable, efficient, and sustainable energy for consumers, protect the competitive energy market, and improve environmental standards.
What are the FERC regulations?
FERC regulations refer to rules and guidelines set by Title 18 of the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR). These regulations govern the energy industry in the United States, including:
- The interstate transmission of electricity, natural gas, and oil.
- The review and approval of energy projects, such as interstate pipelines, natural gas storage facilities, and large hydropower projects.
- The monitoring of energy markets to ensure compliance with FERC rules and to promote fair competition.
- Oversight of environmental matters related to energy projects and operations.
FERC's regulatory domain ensures that the U.S. energy markets operate efficiently, reliably, and fairly, focusing on protecting the public and promoting sustainable energy practices.

What's the difference between FERC vs. NERC?
With so many governing and regulatory bodies in the United States, it can be hard to understand the differences between organizations like the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) and the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC). We explain the differences below:
NERC responsibilities
The North American Electric Reliability Corporation, or NERC, is a non-profit organization responsible for reducing the risks associated with the reliability and security of the electrical grid. NERC’s responsibilities extend to the United States, Canada, and parts of Mexico. In the United States, NERC is subject to the regulations of FERC, and in Canada, NERC must work with governmental authorities, including provincial regulators and the Canadian Electricity Association.
FERC responsibilities
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission, or FERC, regulates the transmission of electricity, natural gas, and oil across state lines. Unlike NERC's focus on the reliability and security of the electric grid, FERC's responsibilities extend to ensuring the efficient and reliable interstate movement of these energy resources. FERC does not have jurisdiction over energy sales directly to consumers, as such transactions fall under the regulatory authority of individual state commissions.
FERC vs. NERC
As outlined above, NERC is a non-profit regulatory body that oversees the reliability and security of the electrical power grid in the United States, Canada, and parts of Mexico. Whereas FERC is a government agency that regulates the interstate transmission of electricity, natural gas, and oil.
The two organizations work closely together, with NERC focusing on the reliability standards for the power grid and FERC providing regulatory oversight and enforcement of these standards. FERC approves the reliability standards proposed by NERC, ensuring they are in alignment with national energy policy and objectives.
What does FERC have to do with corporate finance?
But you may be wondering, how do FERC’s regulations impact corporate finance, and what do you need to be aware of when preparing your financial statements and reports?
Let’s cover how FERC impacts accounting and finance reporting regulations.
Accounting and finance reporting regulations
FERC has established regulatory reporting requirements for its entities in the electric, natural gas, and oil pipeline industries. Companies must abide by the Commission's Uniform System of Accounts (USofA), which standardizes the financial and accounting practices of these entities. This ensures consistency, transparency, and the ability for FERC to effectively oversee and regulate the financial practices within these industries.
Formal accounting guidance
The Commission, alongside its Chief Accountant, offers crucial advice and answers to questions from regulated companies about applying accounting standards set by the Financial Accounting Standards Board. This includes guidance on industry accounting issues and specific company concerns, all framed within the Uniform Systems of Accounts (USofA).
Auditing
FERC audits companies under their jurisdiction to evaluate risk areas, including tariffs, rates, organizational transparency, policies, laws, reliability, and other areas of electric, natural gas, and oil companies. These audits ensure that the energy market operates efficiently, fairly, and reliably, and they help protect consumers from unjust and unreasonable rates and practices.
How is FERC related to ESG?
Recent coverage has highlighted FERC’s critical stance when it comes to Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG), particularly in relation to investor influence in the utility sector. Historically, FERC has scrutinized the financial and operational aspects of utilities to protect consumer interests and ensure the stability and integrity of the energy sector.
And in a statement released in 2023, the Commissioner remarks that, “‘ESG’ investor activity is simply a symptom of a larger, more pernicious threat that has always existed in the utility industry: improper investor influence and control over public utilities.”
FERC further asserts that ESG must go beyond investments, and consider the relationship between investors and the organizations they have control over. In the same statement, the Commissioner says, “Congress may have directed the Commission to streamline its regulations to facilitate greater investments in the utility industry, such as through section 203 blanket authorizations, but that streamlining does not, and should never, come at expense of protecting consumers.”
For these reasons, FERC has concerns about whether such investments prioritize environmental and social goals in a manner that aligns with the commission's mandate to ensure safe, reliable, and economically sound utility services.
Conclusion: Stay current on FERC regulations with Prophix
In wrapping up, we've covered FERC's crucial role within the U.S. energy sector—guiding it towards efficiency, fairness, and sustainability.
We also walked you through FERC's functions, regulations, its distinction from NERC, impact on corporate finance, and its stance on ESG.
With Prophix One, a Financial Performance Platform, managing compliance and staying ahead in regulatory reporting is seamless, ensuring you're always aligned with FERC's evolving standards.