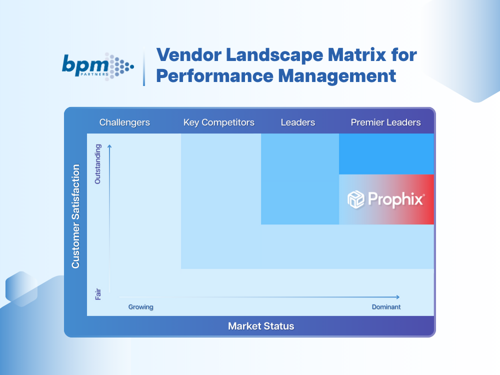
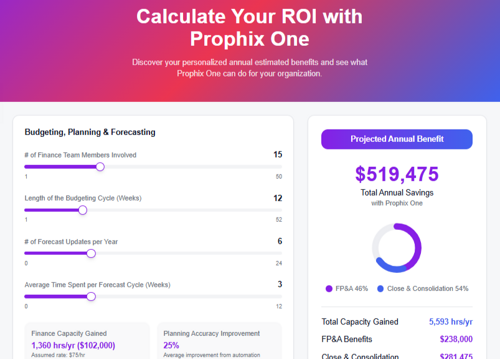
Download the BPM Partners Whitepaper
The comprehensive guide to financial performance management
This ultimate guide covers the key elements, components, and benefits of financial performance management, and how Prophix helps.
December 3, 2024If employee performance is how well that employee uses their skills and knowledge to advance your organization’s goals, financial performance is how your organization does the same with its financial assets.
Optimizing that performance—a practice known as financial performance management—is essential to your organization’s success. That’s because no matter how much revenue a company generates, it won’t get far if its expenses outclass that income due to inefficiencies and misguided strategy.
In this guide to financial performance management, you’ll find:
- A definition of financial performance management
- The 4 elements of financial performance management
- 7 essential components of effective financial performance management
- 4 benefits of financial performance management
What is financial performance management (FPM)?
Financial performance management (FPM) is a strategic approach that involves the use of various processes and tools to monitor, measure, and manage an organization's financial performance. It aims to optimize financial resources and help organizations in achieving their financial objectives. FPM is crucial in making informed decisions, improving efficiency, and driving business growth.
The Office of the CFO can do this by improving processes like account reconciliation, financial consolidation, or financial close, implementing rolling forecasts, or automating finance workflows with financial performance software.
Those who would improve FPM in their organization typically have to contend with processes that depend on a massive amount of manual work, an absence of modern tools, as well as a reliance on spreadsheets and similarly dated methods.
What is financial performance management (FPM) software?
Financial performance management software—like Prophix One—centralizes the Office of the CFO’s essential processes while providing tools to standardize, optimize, and automate them. These platforms allow finance professionals to collaborate on their work seamlessly while having all the financial data they need at their fingertips. FPM software integrates natively with other business systems, like enterprise resource planning (ERP), project management (PM), customer relationship management (CRM), and human resources information (HRIS) platforms to keep all essential data in one place.
Prophix One is just one example of a financial performance management platform that transforms the way the Office of the CFO manages financial processes. Prophix One customers have cut their budgeting time by 50%, saved thousands of hours through automation, and more.
Financial performance management (FPM) vs. enterprise performance management (EPM)
EPM, which can refer to both finance processes and software, is primarily geared towards enterprise organizations. Enterprise organizations are commonly defined as companies with more than 250 employees that operate on an international scale with highly specialized departments.
In contrast, FPM has been specifically developed to support companies of all sizes, including enterprises, and incorporates a broader range of processes, including both finance and accounting functions.
Another difference is that FPM focuses mainly on the financial aspects of performance for finance teams, whereas EPM can often be extended beyond finance to sales, human resources, marketing, and more. And while FPM focuses primarily on finance, many vendors have begun expanding their use cases to include a broader range of operational processes.
FPM stands out for its agility, ease of implementation, and potential cost advantages, particularly for small to medium-sized enterprises. With the addition of cutting-edge analytics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning capabilities, FPM positions itself at the forefront of innovation, ready to empower data-driven decision-making across a variety of business contexts.
When it comes to choosing what’s best for you, overall, you should choose a solution based on your specific organizational needs—rather than strictly by definitions. Consider the scale of your operations, the complexity of your business processes, and your strategic aspirations. For those seeking a solution that not only meets current financial management requirements but also anticipates future challenges with flexibility and foresight, FPM is a compelling choice.

What are the 4 elements of financial performance management?
No matter how you try to improve the way your organization uses its financial assets, your team will typically experience these four elements of FPM:
- Planning: Before you put anything into action, you need to make a plan. This involves forecasting, goal setting, and budgeting.
- Monitoring: Tools like Prophix One allow the Office of the CFO to monitor their organization’s financials dynamically, with live data. Even if you only use spreadsheets and manual data entry, monitoring how your processes impact your plans is essential.
- Reporting: Organizations of a certain size can have dozens of stakeholders involved in each financial process. That’s why financial reporting on the impacts of financial performance management is essential, and a tool that does this for you automatically, like Prophix One, is essential.
- Improving: Every financial process produces a ton of data. That data produces reports, and you can use those reports to find inefficiencies in those processes you can smooth out over time. The smoother your processes, the better your bottom line.
Essential components of effective FPM
Financial performance management is a complex practice full of interconnected parts. Software like Prophix One becomes essential for bringing them all together so you can focus on strategic objectives that drive business growth.
Here are seven of these essential components.
Financial statements
Financial statements tell an important part of the story when it comes to your organization’s finances. Profit and loss statements, balance sheets, cash flow statements, and more are involved in FPM. Being able to quickly—and accurately—produce these statements is crucial.
Key performance indicators
Key performance indicators (or KPIs), allow the Office of the CFO to turn what would otherwise be an overwhelming stream of data into a clear representation of the organization’s financial health. They are specific metrics—like profit margin, revenue per employee, or sales growth—used to accurately track your financials.
Budgeting and forecasting
Budgeting is essential for restricting costs; while forecasting ensures you’re using your financial assets as judiciously as possible. Both of these processes can be extremely time-consuming and resource-intensive, which is why many organizations use FPM platforms like Prophix One.
Data consolidation
Organizations produce massive amounts of data across multiple platforms through day-to-day operations. Proper FPM depends on having a way to consolidate that data—ideally into a single platform—so leaders, technical users, and other experts can all look at the same data.
Risk management
Risk management involves forecasting potential risks that come from a specific course of action, process, or initiative, and finding ways of mitigating their impact. That might mean coming up with specific strategies to counter them or altering initial plans to avoid them completely.
Performance analysis
Key to financial performance management is a frequent review of how your organization’s finances improve—or not—from your efforts. This involves regular reporting, meeting with various stakeholders, and reviewing data.
Continuous monitoring
A financial performance platform, like Prophix One, automatically monitors financial data with dynamic dashboards and automated reports. Whether you have access to one of these tools or not, FPM involves continually monitoring financial KPIs and the Office of the CFO’s various initiatives to see how they affect your bottom line.
Key benefits of financial performance management
FPM involves significant overhauls for many financial processes, but the results more than outweigh the investment. Here are four of the most relevant benefits of FPM.
- Improved decision-making capabilities: FPM involves turning financial data into reports leaders can use to make more informed decisions.
- Enhanced operational efficiency: Through FPM, your organization can optimize the way they use financial assets, eliminating inefficiencies.
- Better alignment of financial strategies with business objectives: A top-down FPM process naturally aligns financial strategies throughout the organization with top-level goals.
- Financial compliance: Keeping organizations compliant is a complex process, but better financial data and smoother processes make this easier.
How to optimize your financial performance management
Financial performance management allows organizations to make the most of their financial assets, reduce costs, and grow their profit margin. Through better reporting, continuous monitoring, and tracking of essential KPIs, the Office of the CFO can put essential financial data within reach of any team, improving alignment between their initiatives and top-level goals.
These processes are made simpler with a fully integrated financial performance management platform like Prophix One, which automatically consolidates the data you need for this essential process.
Are you ready to see what you can do with Prophix One?